Bitcoin?s cycles are changing ? Bloomberg analyst Jamie Coutts explains how and why
Bitcoin Cycles, the world's most popular cryptocurrency, has experienced dramatic price fluctuations since its inception.
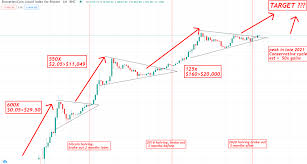
Bitcoin, the world's most popular cryptocurrency, has experienced dramatic price fluctuations since its inception. These fluctuations have often followed a cyclical pattern that has intrigued investors and analysts alike. However, according to Bloomberg analyst Jamie Coutts, Bitcoin's cycles are changing. In this blog post, we will explore why these changes are occurring and what they mean for the future of Bitcoin.
Understanding Bitcoin Cycles
To comprehend why Bitcoin's cycles are changing, we must first understand what these cycles are and how they have traditionally operated.
Bitcoin cycles typically consist of four phases:
- Accumulation: In this phase, savvy investors accumulate Bitcoin at lower prices, often after a significant market downturn.
- Bull Market: The accumulation phase is followed by a bullish market where the price of Bitcoin rises steadily, attracting more investors.
- Distribution: During this phase, early investors and whales begin to sell their holdings, causing price corrections.
- Bear Market: The distribution phase leads to a bear market where Bitcoin's price undergoes a significant decline, leading to fear and panic among investors.
Historically, these cycles have repeated, with varying durations and intensity. Investors and analysts have used these patterns to make informed decisions about when to buy or sell Bitcoin. However, recent developments suggest that these cycles are evolving.
Why Bitcoin's Cycles Are Changing
- Institutional Involvement
One of the primary reasons for the changing nature of Bitcoin cycles is the increasing involvement of institutional investors. Traditionally, Bitcoin was mainly driven by retail investors and early adopters. However, over the past few years, institutions such as hedge funds, corporations, and investment firms have entered the cryptocurrency market.
Institutional investors have brought stability to Bitcoin's price movements. They are less likely to engage in panic selling during market downturns, which can mitigate the severity of bear markets. This institutional involvement is altering the dynamics of Bitcoin cycles, making them less predictable.
- Regulatory Environment
Another factor contributing to the changing Bitcoin cycles is the evolving regulatory landscape. As governments and regulatory bodies worldwide develop frameworks for cryptocurrencies, market dynamics are being influenced.
Regulations can have a significant impact on investor sentiment and market behavior. Clarity in regulations can attract more institutional investors, while uncertainty can lead to market volatility. The evolving regulatory environment adds an element of uncertainty to Bitcoin's cycles.
- Market Maturity
Bitcoin is now more than a decade old, and its market has matured significantly. In its early years, Bitcoin was considered a speculative asset with limited real-world use cases. Today, it is increasingly viewed as a store of value and a hedge against inflation, similar to gold.
The growing recognition of Bitcoin's value and its integration into the traditional financial system have led to changes in market dynamics. The cryptocurrency is now less susceptible to extreme price swings driven solely by sentiment, which can disrupt traditional cycle patterns.
- Technological Advancements
Bitcoin's technology has also evolved over the years. Improvements in scalability, security, and transaction speed have made Bitcoin more efficient and user-friendly. These technological advancements have attracted a broader user base, including institutions and retail investors.
A more user-friendly Bitcoin ecosystem can reduce the likelihood of rapid price fluctuations based on market sentiment, contributing to the changing cycle dynamics.
The Implications of Changing Cycles
So, what do these changing cycles mean for Bitcoin and its investors?
- Reduced Volatility
One of the most significant implications of changing cycles is reduced price volatility. While Bitcoin is still known for its price fluctuations, the peaks and troughs may become less extreme as institutional involvement and market maturity continue to grow. This reduced volatility could make Bitcoin a more appealing asset for conservative investors and institutions.
- Long-Term Investment
With changing cycles, Bitcoin may increasingly be seen as a long-term investment rather than a speculative asset. This shift in perception could lead to more investors holding onto their Bitcoin for extended periods, which, in turn, could stabilize the market further.
- Evolving Strategies
Investors and traders will need to adapt their strategies to the changing cycles. Traditional trading techniques that rely heavily on historical patterns may become less effective. Instead, investors may need to focus on fundamental analysis, news events, and macroeconomic factors that influence Bitcoin's price.
- Increased Scrutiny
As Bitcoin continues to gain legitimacy, it will face increased scrutiny from regulators and policymakers. Investors should stay informed about regulatory changes in their respective jurisdictions to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
Bitcoin's cycles are indeed changing, and the reasons behind this transformation are multifaceted. Institutional involvement, evolving regulations, market maturity, and technological advancements are all contributing factors. While these changes may make Bitcoin's price movements less predictable, they also offer new opportunities for long-term investors and a more stable market overall.
As Bloomberg analyst Jamie Coutts interview suggests, understanding these changes and adapting to them will be crucial for anyone looking to navigate the evolving landscape of Bitcoin and cryptocurrency investments. As the cryptocurrency market continues to mature, it will be fascinating to see how these changes shape the future of Bitcoin and its role in the global financial system.
What's Your Reaction?
















